Linux 命令集合
- Local and Remote Logins
- File System Navigation
- Users and Groups
- File Permissions
- Selinux Permissions
- Process Management
- Updating Software Packages
Local and Remote Logins
The ways of quiting shell Session:
exitcommand- pressing
Ctrl+d
Using SSH Key-based Authentication
- Create an SSH key pair in local server
$ ssh-keygen
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/home/kylin/.ssh/id_rsa): /home/kylin/.ssh/id_t_rsa
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /home/kylin/.ssh/id_t_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /home/kylin/.ssh/id_t_rsa.pub.
...
- Send the SSH public key to the remote server
[kylin@ksoong ~]$ ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_t_rsa.pub root@10.66.218.46
/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
root@10.66.218.46's password:
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh 'root@10.66.218.46'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
- Login into remote server
$ ssh root@10.66.218.46
Creating and Viewing an SoS Report
- If currently working as a non-root user, switch to root.
$ su -
Password:
- Run the sosreport command. This may take many minutes on larger systems.
# sosreport
- Change directory to /var/tmp, and unpack the archive.
# cd /var/tmp
# tar -xvJf sosreport-*.tar.xz
- Change directory to the resulting subdirectory and browse the files found there.
# cd sosreport-ksoong-20160306161748
File System Navigation
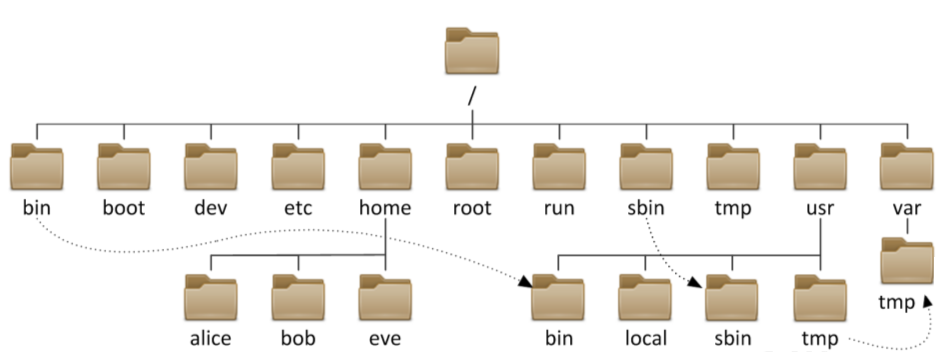
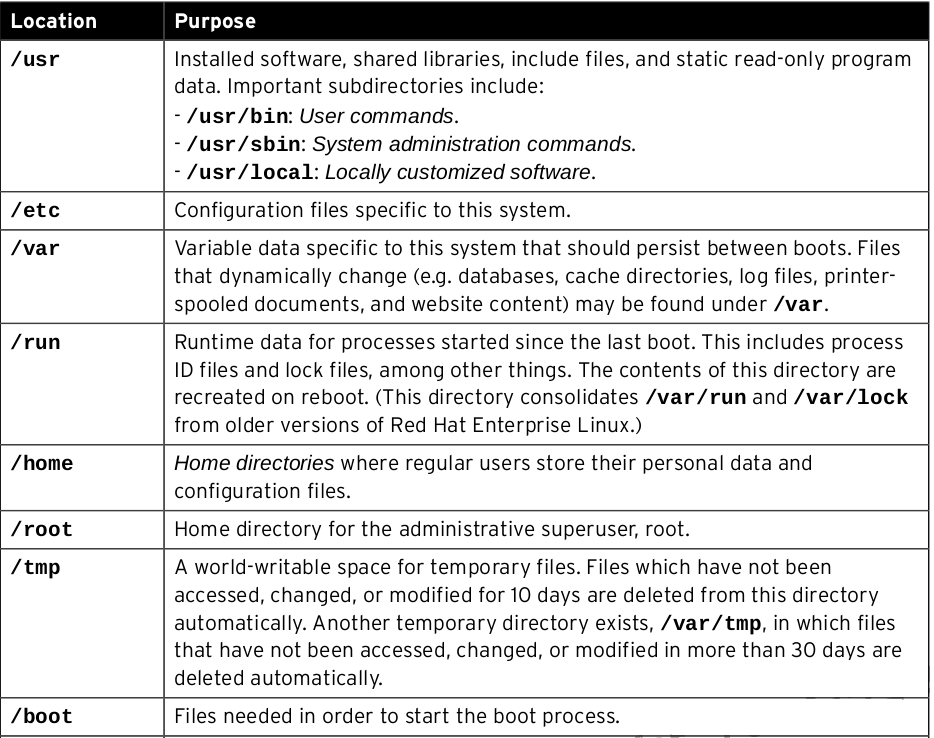
Command-Line File Management
- Create Files
$ touch song1.mp3 song2.mp3 song3.mp3 song4.mp3 song5.mp3
$ touch snap1.jpg snap2.jpg snap3.jpg snap4.jpg snap5.jpg
$ touch film1.avi film2.avi film3.avi film4.avi film5.avi
$ ls -l
- Move Files
$ mv song1.mp3 song2.mp3 song3.mp3 song4.mp3 song5.mp3 Music/
$ mv snap1.jpg snap2.jpg snap3.jpg snap4.jpg snap5.jpg Pictures/
$ mv film1.avi film2.avi film3.avi film4.avi film5.avi Videos/
$ ls -l Music/ Videos/ Pictures/
- Create Directories
$ mkdir friends family work
$ rmdir friends family work
Making Links Between Files
This Section will demonstrate how to use hard links and soft links to make multiple names point to the same file.
- The command
lncreates new hard links to existing files. The command expects an existing file as the first argument, followed by one or more additional hard links. - The
ln -scommand creates a soft link, which is also called a “symbolic link”. A soft link is not a regular file, but a special type of file that points to an existing file or directory. Unlike hard links, soft links can point to a directory, and the target to which a soft link points can be on a different file system.
- Create an additional hard link
# ln /usr/share/doc/qemu/qmp-commands.txt /root/qmp-commands.txt
- Verify the link count on the newly created link
# ls -l /root/qmp-commands.txt
-rw-r--r--. 2 root root 65630 Nov 18 2013 /root/qmp-commands.txt
- Verify the link count on the original file
# ls -l /usr/share/doc/qemu/qmp-commands.txt
-rw-r--r--. 2 root root 65630 Nov 18 2013 /usr/share/doc/qemu/qmp-commands.txt
- Create the soft link
# ln -s /tmp/ /root/tmpdir
- Verify the newly created link with
# ls -l
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 5 Mar 6 16:06 tmpdir -> /tmp/
# cd tmpdir/
# ls -lR
Users and Groups
- /etc/passwd - store information about local users
- /etc/group - store information about local groups
Useful Commands:
$ id
$ ps au
- The id command is used to show information about the current logged-in user.
- The ps command is used to view process information. Add the a option to view all processes with a terminal. To view the user associated with a process, include the u option.
Running Commands as root
- View the user and group information and display the current working directory.
$ id
uid=1000(kylin) gid=1000(kylin) groups=1000(kylin),987(docker) context=unconfined_u:unconfined_r:unconfined_t:s0-s0:c0.c1023
$ pwd
/home/kylin
- View the variables which specify the home directory and the locations searched for executable files.
$ echo $HOME
/home/kylin
$ echo $PATH
/usr/lib64/qt-3.3/bin:/usr/local/bin:/bin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/sbin:/usr/local/rvm/bin:/home/kylin/.local/bin:/home/kylin/bin:/home/kylin/tools/apache-maven-3.2.5/bin:/usr/java/jdk1.8.0_25/bin:/home/kylin/tools/apache-ant-1.9.4/bin:/home/kylin/tools/node-v0.12.6-linux-x64/bin
- Become the root user at the shell prompt.
$ su -
Password:
- View the user and group information and display the current working directory.
# id
uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root) context=unconfined_u:unconfined_r:unconfined_t:s0-s0:c0.c1023
# pwd
/root
- View the variables which specify the home directory and the locations searched for executable files.
# echo $HOME
/root
# echo $PATH
/usr/lib64/qt-3.3/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/.cabal/bin:/usr/local/rvm/bin:/root/bin
- Exit the root
# exit
logout
Creating Users Using Command-line Tools
- Add a user
# adduser student
Execute
tail -2 /etc/passwdcan confirm new added user from file.
- Use the passwd command to add a login password
# passwd student
Managing Groups Using Command-line Tools
- Create a group
# groupadd artists
Execute
tail -5 /etc/groupwill confirm new added group.
- Add a user to a group
# usermod -G student student
# id student
uid=1001(student) gid=1002(student) groups=1002(student)
Managing User Password Aging
- Lock/Unlock a user
# usermod -L student
$ su - student
Password:
su: Authentication failure
# usermod -U student
$ su - student
Password:
Last login: Tue Mar 8 15:30:03 CST 2016 on pts/1
Last failed login: Tue Mar 8 15:30:41 CST 2016 on pts/3
There was 1 failed login attempt since the last successful login.
- Change the password policy to require a new password every 90 days
# chage -M 90 student
# chage -l student
Last password change : Mar 08, 2016
Password expires : Jun 06, 2016
Password inactive : never
Account expires : never
Minimum number of days between password change : 0
Maximum number of days between password change : 90
Number of days of warning before password expires : 7
Using Identity Management Services
//TODO–
File Permissions
Managing File Security from the Command Line
- login to root, create a directory
# mkdir /home/kylin-text
- Change the group ownership to kylin
# chown :kylin /home/kylin-text/
- Ensure the permissions of kylin-text allows group members to create and delete files.
# chmod g+w /home/kylin-text/
- Ensure the permissions of ateam-text forbids others from accessing its files.
# chmod 770 /home/kylin-text/
# ls -ld /home/kylin-text/
- Verify the setting
# exit
logout
$ cd /home/kylin-text/
$ touch samplefile1
$ ls -l samplefile1
-rw-rw-r--. 1 kylin kylin 0 Mar 10 11:27 samplefile1
Controlling New File Permissions and Ownership
- show umask
[student@ksoong ~]$ umask
0002
- check default umask affects permissions
[student@ksoong ~]$ mkdir /tmp/shared
[student@ksoong ~]$ ls -ld /tmp/shared/
drwxrwxr-x. 2 student student 40 Mar 10 11:46 /tmp/shared/
[student@ksoong ~]$ touch /tmp/shared/defaults
[student@ksoong ~]$ ls -l /tmp/shared/defaults
-rw-rw-r--. 1 student student 0 Mar 10 11:47 /tmp/shared/defaults
- do some change
[student@ksoong ~]$ chmod g+s /tmp/shared/
[student@ksoong ~]$ ls -ld /tmp/shared/
drwxrwsr-x. 2 student student 60 Mar 10 11:47 /tmp/shared/
[student@ksoong ~]$ umask 27
[student@ksoong ~]$ touch /tmp/shared/sameplefile2
[student@ksoong ~]$ ls -l /tmp/shared/sameplefile2
-rw-r-----. 1 student student 0 Mar 10 11:52 /tmp/shared/sameplefile2
[student@ksoong ~]$ umask
0027
[student@ksoong ~]$ umask 7
POSIX Access Control Lists (ACLs)
- View file ACLs
$ getfacl gcviewer.properties
# file: gcviewer.properties
# owner: kylin
# group: kylin
user::rw-
group::rw-
other::r--
Using ACLs to Grant and Limit Access
//TODO–
Selinux Permissions
//TODO–
Process Management
Killing Processes
- Start 3 processes
$ (while true; do echo -n "game " >> ~/outfile; sleep 1; done) &
$ (while true; do echo -n "set " >> ~/outfile; sleep 1; done) &
$ (while true; do echo -n "match " >> ~/outfile; sleep 1; done) &
- Check all running processes
$ tail -f outfile
$ jobs
[1] Running ( while true; do
echo -n "game " >> ~/outfile; sleep 1;
done ) &
[2]- Running ( while true; do
echo -n "set " >> ~/outfile; sleep 1;
done ) &
[3]+ Running ( while true; do
echo -n "match " >> ~/outfile; sleep 1;
done ) &
- Kill process
$ kill -SIGTERM 7174
$ kill -SIGTERM 7187
$ kill -SIGTERM 7220
Monitoring Process Activity
- Check cpu info
$ grep "model name" /proc/cpuinfo
model name : Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-4200U CPU @ 1.60GHz
model name : Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-4200U CPU @ 1.60GHz
model name : Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-4200U CPU @ 1.60GHz
model name : Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-4200U CPU @ 1.60GHz
$ grep "model name" /proc/cpuinfo | wc -l
4
- top commands
top
$ top -H -p 16943