Netty 4 源码分析
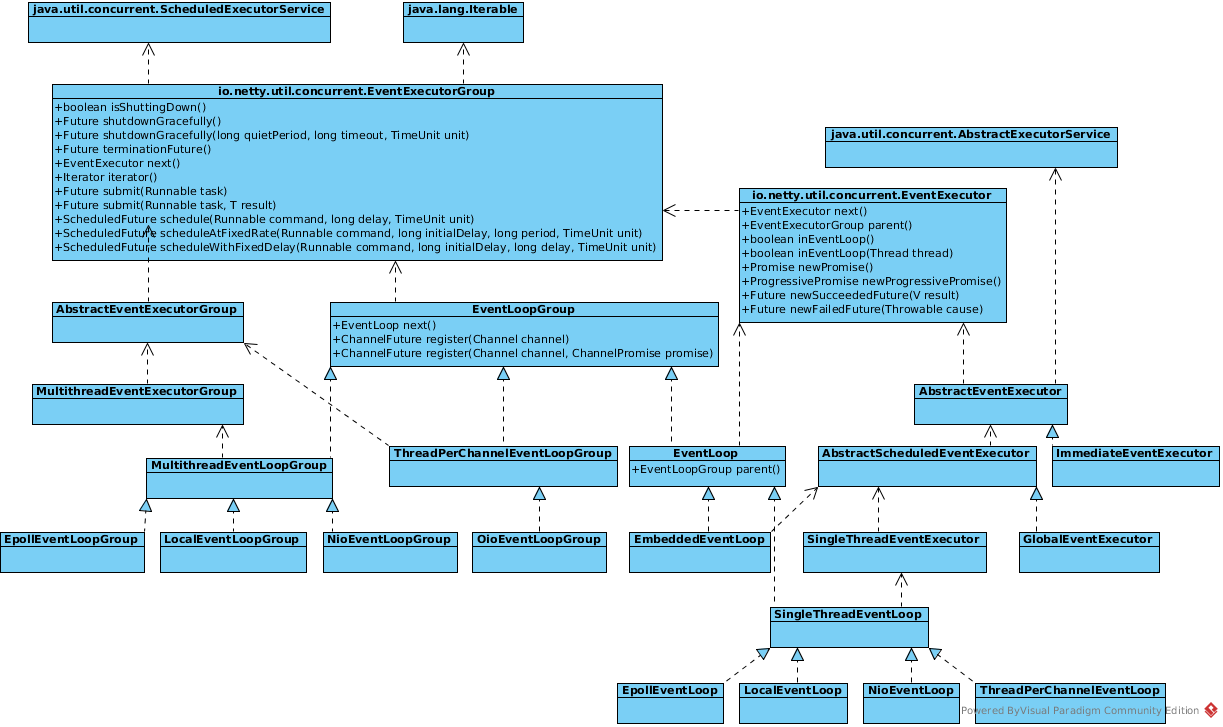
EventLoopGroup
API Usage Example:
NamedThreadFactory nettyPool = new NamedThreadFactory("NIO");
int maxWorkers = Math.max(4, 2 * Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
SelectorProvider provider = SelectorProvider.provider();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(maxWorkers, nettyPool, provider);
一个 EventLoopGroup 实际就是一个 EventLoop 线程组,负责管理 EventLoop 的申请和释放。EventLoopGroup 管理的线程数可以通过构造函数设置,如果没有设置,默认取-Dio.netty.eventLoopThreads, 如果该系统参数也没有指定,则为可用的CPU内核数 × 2。
Bootstrap
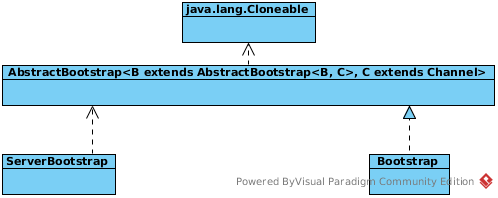
A Bootstrap class is a helper class that makes it easy to bootstrap a Channel. It contains two implementation, ServerBootstrap and Bootstrap, in the following secion we will use Netty Echo Example to explain the Bootstrap.
ServerBootstrap
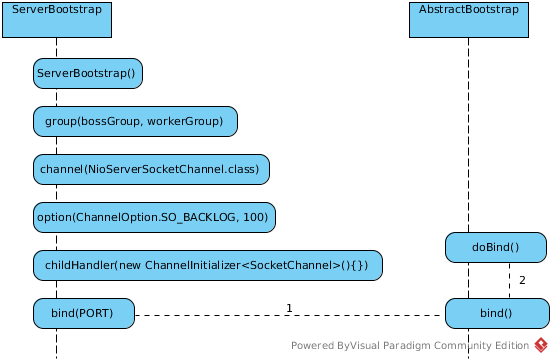
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 100)
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>(){
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline p = ch.pipeline();
p.addLast(new EchoServerHandler());
}});
ChannelFuture f = bootstrap.bind(PORT).sync();
通常情况下,服务端的创建是在用户进程启动的时候进行,因此一般由Main函数或者启动类负责创建,服务端的创建由业务线程负责完成。在创建服务端的时候实例化了2个EventLoopGroup,bossGroup 和 workerGroup:
- bossGroup 线程组实际就是 Acceptor 线程池,负责处理客户端的 TCP 连接请求,如果系统只有一个服务端端口需要监听,则建议 bossGroup 线程组线程数设置为 1。
- workerGroup是真正负责I/O读写操作的线程组,通过ServerBootstrap的group方法进行设置,用于后续的Channel绑定。