Understanding Teiid Metadata
- What is Teiid Metadata
- SystemMetadata loading in VDBRepository startup
- Metadata operations in VDB deploying
- Examples
What is Teiid Metadata
Teiid Metadata like other database(mysql, oracle) metadata, like below figure,
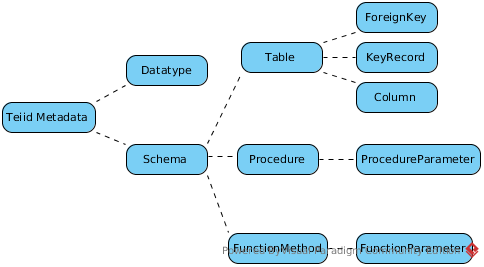
From functional categories teiid metadata contain
- Schemas - The Schema contain tables, procedures, functions; the Table contain primary key, foreign key, unique key, columns, etc; The Procedure contain Procedure parameter; the Function contain function parameter.
- Datatypes - types.dat are used to define teiid datatypes
From scope/administation categories teiid metadata contain
- System defined Metadata - SystemMetadata loading in VDBRepository startup
- User defined Metadata - Metadata operations in VDB deploying
SQL examples for Teiid Metadata Administration
Get all Schemas of a specific VDB
SELECT Name FROM SYS.Schemas WHERE VDBName = 'Portfolio'
Get all Tables of a specific VDB and Schema
SELECT Name FROM SYS.Tables WHERE SchemaName = 'Accounts' AND VDBName = 'Portfolio'
Get all teiid supported datatypes
SELECT TypeName, JavaClass, RuntimeType FROM SYS.DataTypes
SystemMetadata loading in VDBRepository startup
In Teiid, every VDB reference a VDBRepository, once VDBRepository startup, it will load System Metadata, SystemMetadata is the API to operate with SystemMetadata:
SystemMetadata.getInstance().getSystemStore();
The System Metadata defined in types.dat, SYS.sql, SYSADMIN.sql, the loading order like:
- types.dat - define all supported datatypes
- SYS.sql - Contain System Tables: Columns, DataTypes, KeyColumns, Keys, ProcedureParams, Procedures, FunctionParams, Functions, Properties, ReferenceKeyColumns, Schemas, Tables, VirtualDatabases; System Procedures: getXMLSchemas, ARRAYITERATE; System Views: spatial_ref_sys, GEOMETRY_COLUMNS
- SYSADMIN.sql - Contain Tables: Usage, MatViews, VDBResources, Triggers, Views, StoredProcedures; Procedures: isLoggable, logMsg, refreshMatView, refreshMatViewRow, refreshMatViewRows, setColumnStats, setProperty, setTableStats, matViewStatus, loadMatView, updateMatView
Metadata operations in VDB deploying
There are 3 phases of Metadata operations in VDB deploying:
- Assign Metadata Repositories
- Metadata loading
- VDB finish deploy
Assign Metadata Repositories
Assign Metadata Repositories means assign a MetadataRepository to each Model which contained in a VDB definition. Assuming a VDB contain 4 Models and the processing of assign Metadata Repositories likes
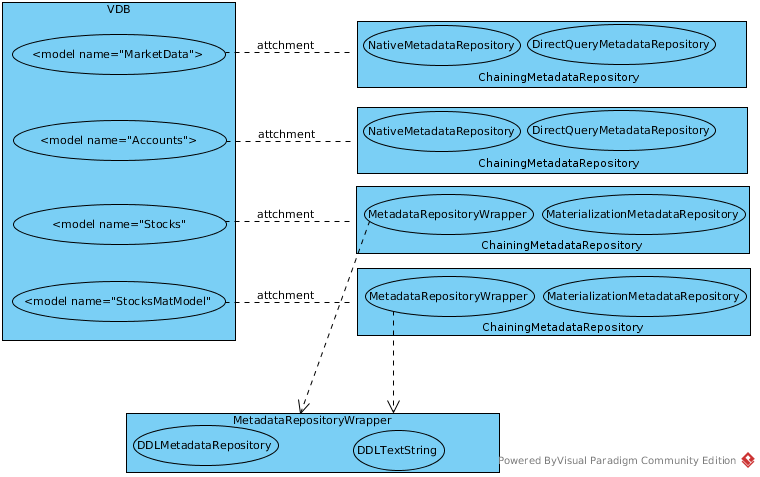
As above figure, the VDB contain 4 Models:
MarketData- define a source point to a csv file, which assigned a ChainingMetadataRepository contain a NativeMetadataRepository and a DirectQueryMetadataRepositoryAccounts- define a source point to a RDBMS, which assigned a ChainingMetadataRepository contain a NativeMetadataRepository and a DirectQueryMetadataRepositoryStocks- is a virtual model, contains a DDL text metadata, which assigned a ChainingMetadataRepository contain a MetadataRepositoryWrapper and a MaterializationMetadataRepository, a MetadataRepositoryWrapper contain a DDLMetadataRepository and DDL Text StringStocksMatModel- is a virtual model, contains a DDL text metadata, which assigned a ChainingMetadataRepository contain a MetadataRepositoryWrapper and a MaterializationMetadataRepository, a MetadataRepositoryWrapper contain a DDLMetadataRepository and DDL Text String
All ChainingMetadataRepository, NativeMetadataRepository, DirectQueryMetadataRepository, MetadataRepositoryWrapper, DDLMetadataRepository and MaterializationMetadataRepository are sub-class of MetadataRepository, more details refer to UML diagram.
Metadata loading
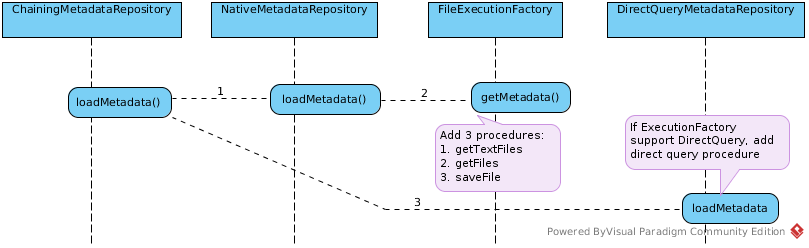
Once Assign Metadata Repositories finished, each Model has reference a MetadataRepository, each of them’s loadMetadata() methods be invoked iteratively, continue the VDB in Assign Metadata Repositories, the following is the 4 models load metadata sequence diagram:
MarketData Load Metadata
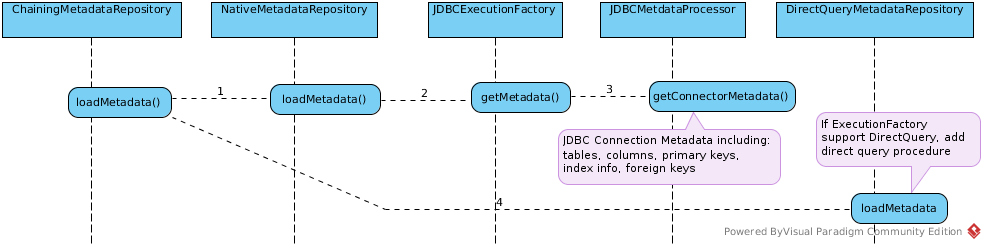
Accounts Load Metadata
- Before loading metadada, a
MetadataFactory,ExecutionFactory(only for Source Model) andConnectionFactory(only for Source Model) be created, passed as the parameters of ChainingMetadataRepository’s loadMetadata() method. - Loading metadata, will load all source metadata(tables, columns, primary keys, index info, foreign keys) into
MetadataFactory. - After load metadata, MetadataFactory’s
mergeInto (MetadataStore store)be invoked, MetadataFactory’s metadata be merged into a VDB scope MetadataStore.
Stocks/StocksMatModel Load Metadata
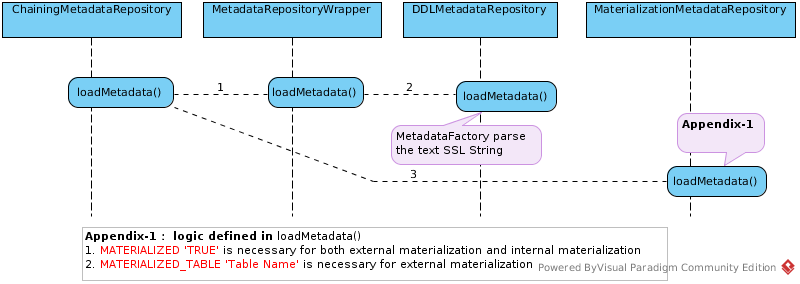
- Before loading metadada, a
MetadataFactorybe created - Loading metadata, in DDLMetadataRepository, MetadataFactory’s parse() invoked, parse the ddl text to Tables and Columns, a example refer to Example.2 MetadataFactory parse ddl text
- After load metadata, MetadataFactory’s
mergeInto (MetadataStore store)be invoked, MetadataFactory’s metadata be merged into a VDB scope MetadataStore.
A MetadataFactory used in each Model’s Metadata loading, MetadataFactory can merge into a global VDB scope MetadataStore, which contains dataTypes, vdbResources, grants and a Schema, related with tables, procedures, functions.
Note that, the result of Metadata loading load all metadata to a VDB scope MetadataStore, metadata in MetadataStore saved by Schema(each Model in VDB reference a Schema).
Once the last Model’s Metadata loading finished, VDBRepository’s finishDeployment() will be invoked, relate below section for more.
VDB finish deploy
As below figure, the VDB finish deploy mainly contains:
- init runtime metadata API and attach it to VDB
- validate the DDL SQL String which exist in VDB’s virtual model
- invoke VDBLifeCycleListener’s finishedDeployment()
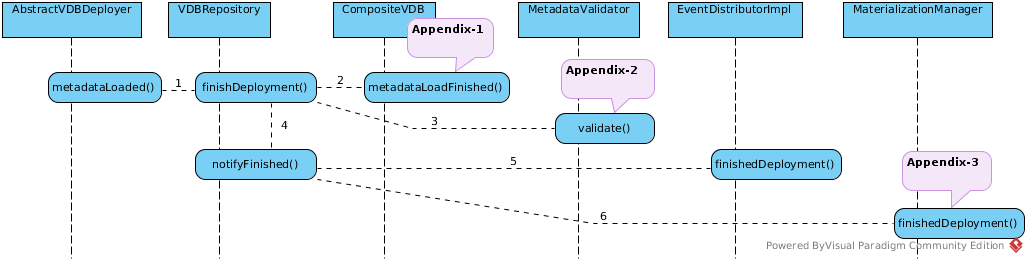
Appendix-1: buildTransformationMetaData()
Build runtime metadata API QueryMetadataInterface1’s implementation TransformationMetadata, this interface used by query components in runtime to access metadata. This implementation related with a VDB via VDB attachment:
TransformationMetadata metadata = buildTransformationMetaData(mergedVDB, getVisibilityMap(), mergedStore, getUDF(), systemFunctions, this.additionalStores);
QueryMetadataInterface qmi = metadata;
mergedVDB.addAttchment(QueryMetadataInterface.class, qmi);
mergedVDB.addAttchment(TransformationMetadata.class, metadata);
mergedVDB.addAttchment(MetadataStore.class, mergedStore);
NOTE:
TransformationMetadatabase on VDB Scope MetadataMetadataStore, bothTransformationMetadataandMetadataStorebe added as VDB attachment.
Appendix-2: Metadata Validator
Validate all Metadata existed in Global VDB Scope MetadataStore with the following MetadataRule:
- SourceModelArtifacts - do not allow foreign tables, source functions in view model and vice versa
- CrossSchemaResolver - resolves the artifacts that are dependent upon objects from other schemas materialization sources, fk and data types, ensures that even if cached metadata is used that we resolve to a single instance
- ResolveQueryPlans - Resolves metadata query plans to make sure they are accurate
- MinimalMetadata - At minimum the model must have table/view, procedure or function
- MatViewPropertiesValidator - Validate the Materrialization Properties
Appendix-3: MaterializationManager
Refer to teiid-mat-view.
Examples
This section contain examples to quick understand the Teiid Metadata.
Example.1: Load classpath ddl file
Assuming customer.ddl file under classpath, which define a series of Metadata, this example demonstrates how to load metadata from a classpath file.
VDBMetaData vdb = new VDBMetaData();
vdb.setName("ExampleVDB");
vdb.setVersion(1);
Properties p = new Properties();
QueryParser parser = new QueryParser();
Map<String, Datatype> typeMap = SystemMetadata.getInstance().getRuntimeTypeMap();
ModelMetaData mmd = new ModelMetaData();
mmd.setName("ExampleMode");
vdb.addModel(mmd);
MetadataFactory factory = new MetadataFactory(vdb.getName(), vdb.getVersion(), "ExampleMode", typeMap, p, null);
parser.parseDDL(factory, loadReader("customer.ddl"));
MetadataStore systemStore = factory.asMetadataStore();
TransformationMetadata tm = new TransformationMetadata(vdb, new CompositeMetadataStore(systemStore), null, new SystemFunctionManager(typeMap).getSystemFunctions(), null);
vdb.addAttchment(QueryMetadataInterface.class, tm);
MetadataValidator validator = new MetadataValidator(typeMap, parser);
ValidatorReport report = validator.validate(vdb, systemStore);
if (report.hasItems()) {
throw new TeiidRuntimeException(report.getFailureMessage());
}
Example.2 MetadataFactory parse ddl text
Sample DDL Text File contain dll text, this example will demonstrate how MetadataFactory parse ddl text.
ModelMetaData mmd = new ModelMetaData();
mmd.setName("ExampleMode");
MetadataFactory factory = new MetadataFactory("VDB", "1", datatypes, mmd);
factory.setBuiltinDataTypes(SystemMetadata.getInstance().getRuntimeTypeMap());
factory.getSchema().setPhysical(false);
factory.setParser(new QueryParser());
factory.parse(new StringReader(ddl));
for (Table t :factory.getSchema().getTables().values()) {
List<Column> matViewColumns = t.getColumns();
for(int i = 0 ; i < matViewColumns.size() ; i ++){
Column c = matViewColumns.get(i);
System.out.println(c.getName() + ", " + c.getDatatype());
}
System.out.println(t.getProperty("{http://www.teiid.org/ext/relational/2012}MATVIEW_STATUS_TABLE", false));
}
Run code will output:
id, Datatype name=string, basetype name=anySimpleType, runtimeType=string, javaClassName=java.lang.String, ObjectID=mmuuid:bf6c34c0-c442-1e24-9b01-c8207cd53eb7
a, Datatype name=string, basetype name=anySimpleType, runtimeType=string, javaClassName=java.lang.String, ObjectID=mmuuid:bf6c34c0-c442-1e24-9b01-c8207cd53eb7
b, Datatype name=string, basetype name=anySimpleType, runtimeType=string, javaClassName=java.lang.String, ObjectID=mmuuid:bf6c34c0-c442-1e24-9b01-c8207cd53eb7
c, Datatype name=string, basetype name=anySimpleType, runtimeType=string, javaClassName=java.lang.String, ObjectID=mmuuid:bf6c34c0-c442-1e24-9b01-c8207cd53eb7
status