Java ThreadLocal
什么是 Java ThreadLocal
From Oracle JavaSE 8 api doc:
java.lang.ThreadLocal class provides thread-local variables. These variables differ from their normal counterparts in that each thread that accesses one (via its get() or set() method)has its own, independently initialized copy of the variable.
Java ThreadLocal instances are typically private static fields in classes that wish to associate state with a thread (e.g., a user ID or Transaction ID).
For example, the class below generates unique identifiers local to each thread. A thread’s id is assigned the first time it invokes ThreadId.get() and remains unchanged on subsequent calls.
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class ThreadId {
private static final AtomicInteger nextId = new AtomicInteger(0);
private static final ThreadLocal<Integer> threadId = new ThreadLocal<Integer>(){
protected Integer initialValue() {
return nextId.getAndIncrement();
}};
public static int get(){
return threadId.get();
}
}
Each thread holds an implicit reference to its copy of a thread-local variable as long as the thread is alive and the ThreadLocal instance is accessible; after a thread goes away, all of its copies of thread-local instances are subject to garbage collection (unless other references to these copies exist).
ThreadLocal 原理
结合上面示例中 ThreadId 类,我们运行如下代码
for(int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i ++){
System.out.print(ThreadId.get() + ' ');
}
输出结果为
0 0 0
接下来我们结合如上运行结果分析 ThreadLocal 工作原理
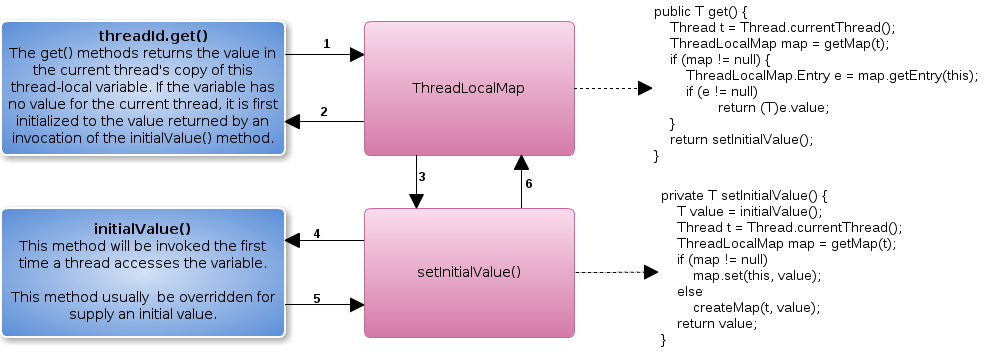
- 从 ThreadLocalMap 中获取Entry
- 如果Entry存在返回相对应的value
- 如果Entry不在在,调运setInitialValue()
- setInitialValue()调运被重写的方法initialValue()
- initialValue()返回初始化value,
- setInitialValue()将其添加到 ThreadLocalMap,并返回