HBase Data Model
In HBase, data is stored in tables, which have rows and columns. The below figure show completed Data Model Terminology:
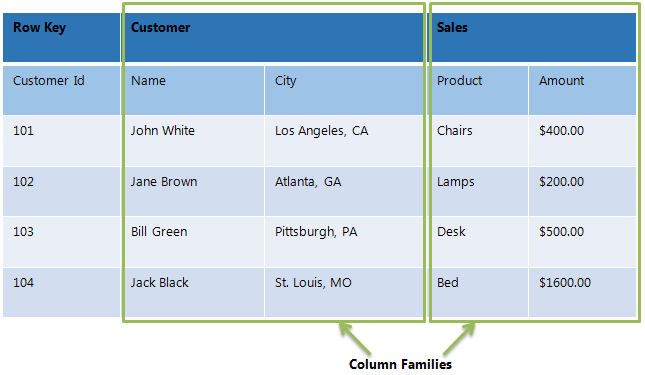
- Table - An HBase table consists of multiple rows.
- Row - A row in HBase consists of a row key and one or more columns with values associated with them. Rows are sorted alphabetically by the row key as they are stored.
- Column - A column in HBase consists of a column family and a column qualifier, which are delimited by a : (colon) character.
- Column Family - Column families physically colocate a set of columns and their values, often for performance reasons. Each column family has a set of storage properties, such as whether its values should be cached in memory, how its data is compressed or its row keys are encoded, and others. Each row in a table has the same column families. Column families are specified when you create your table, and influence the way your data is stored in the underlying filesystem.
- Column Qualifier - A column qualifier is added to a column family to provide the index for a given piece of data. Given a column family
content, a column qualifier might becontent:html, and another might becontent:pdf. - Cell - A cell is a combination of row, column family, and column qualifier, and contains a value and a timestamp, which represents the value’s version.
- Timestamp - A timestamp is written alongside each value, and is the identifier for a given version of a value.
Java Example to show HBase Data Model
We will create a example exact like above figure, which a table names Customer, with 2 Column Family customer and sales, each Column Family contain 2 columns.
Example prerequisite:
- HBase be installed and started
- hbase-client liabaries, if use maven, add dependency as below:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbase</groupId>
<artifactId>hbase-client</artifactId>
<version>0.98.8-hadoop2</version>
</dependency>
Create Table Customer
The following code shows how create Table Customer with 2 Column Familys customer and sales:
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
HBaseAdmin admin = new HBaseAdmin(conf);
HTableDescriptor tableDescriptor = new HTableDescriptor(TableName.valueOf("Customer"));
tableDescriptor.addFamily(new HColumnDescriptor("customer"));
tableDescriptor.addFamily(new HColumnDescriptor("sales"));
admin.createTable(tableDescriptor);
Put 4 rows to Customer
The following code show put 4 rows to Table Customer, with row id 101, 102, 103, 103 respectively:
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
HTable table = new HTable(conf, "Customer");
Put put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes("101"));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("customer"), Bytes.toBytes("name"), Bytes.toBytes("John White"));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("customer"), Bytes.toBytes("city"), Bytes.toBytes("Los Angeles, CA"));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("sales"), Bytes.toBytes("product"), Bytes.toBytes("Chairs"));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("sales"), Bytes.toBytes("amount"), Bytes.toBytes("$400.00"));
table.put(put);
table.flushCommits();
put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes("102"));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("customer"), Bytes.toBytes("name"), Bytes.toBytes("Jane Brown"));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("customer"), Bytes.toBytes("city"), Bytes.toBytes("Atlanta, GA"));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("sales"), Bytes.toBytes("product"), Bytes.toBytes("Lamps"));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("sales"), Bytes.toBytes("amount"), Bytes.toBytes("$200.00"));
table.put(put);
table.flushCommits();
put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes("103"));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("customer"), Bytes.toBytes("name"), Bytes.toBytes("Bill Green"));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("customer"), Bytes.toBytes("city"), Bytes.toBytes("Pittsburgh, PA"));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("sales"), Bytes.toBytes("product"), Bytes.toBytes("Desk"));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("sales"), Bytes.toBytes("amount"), Bytes.toBytes("$500.00"));
table.put(put);
table.flushCommits();
put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes("104"));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("customer"), Bytes.toBytes("name"), Bytes.toBytes("Jack Black"));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("customer"), Bytes.toBytes("city"), Bytes.toBytes("St. Louis, MO"));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("sales"), Bytes.toBytes("product"), Bytes.toBytes("Bed"));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("sales"), Bytes.toBytes("amount"), Bytes.toBytes("$1600.00"));
table.put(put);
table.flushCommits();
table.close();
Scan Table
The code below shoe scan Table:
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
HTable table = new HTable(conf, "Customer");
Scan scan = new Scan();
ResultScanner rs = table.getScanner(scan);
try {
for (Result r = rs.next(); r != null; r = rs.next()){
printResult(r);
}
} finally {
rs.close();
}
table.close();
private static void printResult(Result result) {
String row = Bytes.toString(result.getRow());
System.out.println(row);
for(byte[] key : result.getMap().keySet()) {
String family = Bytes.toString(key);
System.out.println("\t" + family);
NavigableMap<byte[], NavigableMap<Long, byte[]>> value = result.getMap().get(key);
for(byte[] qualifier : value.keySet()) {
System.out.println("\t\t" + Bytes.toString(qualifier));
NavigableMap<Long, byte[]> cell = value.get(qualifier);
for(Long timestamp : cell.keySet()) {
String cellValue = Bytes.toString(cell.get(timestamp));
System.out.printf("\t\t\t%s, %d\n", cellValue, timestamp);
}
}
}
}
Run above code the console output like:
101
customer
city
Los Angeles, CA, 1417409512824
name
John White, 1417409512824
sales
amount
$400.00, 1417409512824
product
Chairs, 1417409512824
102
customer
city
Atlanta, GA, 1417409512856
name
Jane Brown, 1417409512856
sales
amount
$200.00, 1417409512856
product
Lamps, 1417409512856
103
customer
city
Pittsburgh, PA, 1417409512864
name
Bill Green, 1417409512864
sales
amount
$500.00, 1417409512864
product
Desk, 1417409512864
104
customer
city
St. Louis, MO, 1417409512871
name
Jack Black, 1417409512871
sales
amount
$1600.00, 1417409512871
product
Bed, 1417409512871
Get one row from Table
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
HTable table = new HTable(conf, "Customer");
Get get = new Get("101".getBytes());
get.addFamily("customer".getBytes());
Result result = table.get(get);
for(Cell cell : result.rawCells()) {
System.out.println(new String(CellUtil.cloneValue(cell)) + " - " + cell.getTimestamp());
}
table.close();
Run above code to get row 101, the output like:
Los Angeles, CA - 1417409512824
John White - 1417409512824
Delete Table
Run below code to delete Table:
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
HBaseAdmin admin = new HBaseAdmin(conf);
admin.disableTable("Customer");
admin.deleteTable("Customer");