Understanding database Views
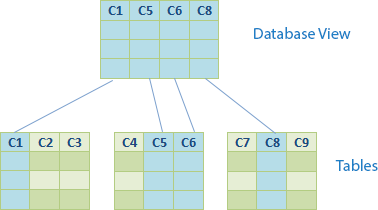
In database theory, a view is a virtual table or a **logical table ** which based on the result-set of an SQL statement. A view contains rows and columns, just like a real table. The fields in a view are fields from one or more real tables in the database, the below figure show database view field C1 come from real table Table1, C5, C6 come from real table Table2 and C8 come from real table Table3:
You can add SQL functions, WHERE, and JOIN statements to a view and present the data as if the data were coming from one single table.
Because a database view is similar to a database table, which consists of rows and columns, so you can query data against it. Most database management systems, including MySQL, allows you to update data in the underlying tables through the database view with some prerequisites.
SQL CREATE VIEW Statement
Refer to w3schools sql view
Advantages of database view
The following are advantages of using database views:
-
A database view allows you to simplify complex queries: a database view is defined by an SQL statement that associates with many underlying tables. You can use database view to hide the complexity of underlying tables to the end-users and external applications. Through a database view, you only have to use simple SQL statements instead of complex ones with many joins.
-
A database view helps limit data access to specific users. You may not want a subset of sensitive data can be queryable by all users. You can use database views to expose only non-sensitive data to a specific group of users.
-
A database view provides extra security layer. Security is a vital part of any relational database management system. Database views provides extra security for a database management system. A database view allows you to create only read-only view to expose read-only data to specific users. Users can only retrieve data in read-only view but cannot update it.
-
A database view enables computed columns. A database table should not have calculated columns however a database view should. Suppose in the
orderDetailstable you havequantityOrder(the number of ordered products) andpriceEach(price per product item) columns. However theorderDetailstable does not have computed column to store total sales for each line item of the order. If it has, the database schema would not be a good design. In this case, you can create a computed column namedtotal, which is a product ofquantityOrderandpriceEachto store the computed result. When you query data from the database view, the data of the computed column is calculated on fly. -
Database view enables backward compatibility. Suppose you have a central database, which many applications are using it. One day you decided to redesign the database to adapt with the new business requirements. You remove some tables and create several new tables, and you don’t want the changes affect other applications. In this scenario, you can create database views with the same schema as the legacy tables that you’ve removed.
Disadvantages of database view
Besides the advantages above, there are several disadvantages of using database views:
-
Performance: querying data from a database view can be slow especially if the view is created based on other views.
-
Tables dependency: you create view based on underlying tables of the a database. Whenever you change the structure of those tables that view associates with, you have to change the view as well.