Java Transaction API and Examples
This page contain examples of Java Transaction API.
TransactionManager

The javax.transaction.TransactionManager interface defines the methods that allow an application server to manage transactions on behalf of the applications.
User applications should not use this interface directly, but use UserTransaction insted if they need to do their own transaction management.
Internally, the transaction manager associates transactions with threads, and the methods here operate on the transaction associated with the calling thread.
Example.1: begin(), commit()
TransactionManager tm = getTransactionManager();
tm.begin();
tm.commit();
Example.2: begin(), rollback()
TransactionManager tm = getTransactionManager();
tm.begin();
tm.rollback();
Example.3: begin(), setRollbackOnly(), commit()
TransactionManager tm = getTransactionManager();
tm.begin();
tm.setRollbackOnly();
tm.commit();
NOTE: this will throw
javax.transaction.RollbackException
Example.4: begin(), getStatus(), commit()
TransactionManager tm = getTransactionManager();
tm.begin();
System.out.println(Status.STATUS_ACTIVE == tm.getStatus());
tm.commit();
System.out.println(Status.STATUS_NO_TRANSACTION == tm.getStatus());
Run this code will output:
true
true
Example.5: setTransactionTimeout(), begin(), commit()
TransactionManager tm = getTransactionManager();
tm.setTransactionTimeout(3);
tm.begin();
Thread.sleep(1000 * 5);
tm.commit();
NOTE: this will throw
javax.transaction.RollbackException
Example.6: begin(), getTransaction()
TransactionManager tm = getTransactionManager();
tm.begin();
Transaction t = tm.getTransaction();
UserTransaction
//TODO
Synchronization
The The transaction manager supports a javax.transaction.Synchronization that allows the interested party to be notified before and after the transaction completes. Using the registerSynchronization method, the application server registers a Synchronization object for the transaction currently associated with the target Transaction object.
Example.1: Print notes before and after the transaction completes
TransactionManager tm = getTransactionManager();
tm.begin();
Transaction t = tm.getTransaction();
t.registerSynchronization(new Synchronization(){
public void beforeCompletion() {
System.out.println("transaction before completion");
}
public void afterCompletion(int status) {
System.out.println("transaction after completion, status: " + status);
}
});
tm.commit();
Run this code will output:
transaction before completion
transaction after completion, status: 3
NOTE: status is 3 means
STATUS_COMMITTED.
XAResource
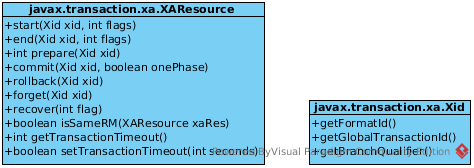
The javax.transaction.xa.XAResource interface is a Java mapping of the industry standard XA interface based on the X/Open CAE Specification (Distributed Transaction Processing: The XA Specification).
The XA interface defines the contract between a Resource Manager and a Transaction Manager in a distributed transaction processing (DTP) environment. An XA resource such as a JDBC driver or a JMS provider implements this interface to support association between a global transaction and a database or message service connection.
The XAResource interface can be supported by any transactional resource that is intended to be used by application programs in an environment where transactions are controlled by an external transaction manager. An example of such a resource is a database management system. An application may access data through multiple database connections. Each database connection is enlisted with the transaction manager as a transactional resource. The transaction manager obtains an XAResource for each connection participating in a global transaction. The transaction manager uses the start(Xid, int) method to associate the global transaction with the resource, and it uses the end(Xid, int) method to disassociate the transaction from the resource. The resource manager is responsible for associating the global transaction to all work performed on its data between the start and end method invocation.
At transaction commit time, the resource managers are informed by the transaction manager to prepare, commit, or rollback a transaction according to the two-phase commit protocol.
Behind the resources that implement this interface the resource manager exists. The resource manager does not have a public interface or direct references, and can manage several resources. To see if two resources are managed by the same resource manager, the isSameRM(XAResource) method can be used.
The Xid interface is a Java mapping of the X/Open transaction identifier XID structure. A transaction id is an aggregate of three parts:
- The format identifier indicates the transaction family and tells how the other two parts should be interpreted.
- The global transaction id denotes, with the format specifier, the id of the global transaction.
- The branch qualifier denotes a particular branch of the global transaction.
The Xid interface is used by the application server, the transaction manager and the resource managers, and is not used in application programs.